Geoprocessing with ArcGIS
The most
important thing to understand about geoprocessing in ArcGIS is that all geoprocessing
operations involve the use of tools. You've already seen how to run a tool from
its dialog, but there is more than one way to perform geoprocessing.
You can use a tool's dialog, the command line, a model, or a script, depending
on your needs or preferences.
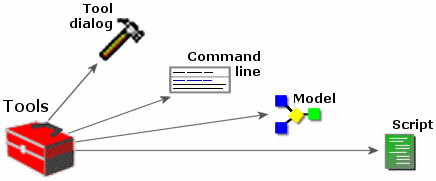
The ArcGIS
geoprocessing framework provides multiple ways of
working.
You can run
any geoprocessing tool using any method in either ArcMap or ArcCatalog™. If you
have the 3D Analyst extension, you can also run these tools in ArcGlobe™ and ArcScene™. In this
course, you will only work with ArcCatalog and ArcMap.
![]() Which application is best for geoprocessing?
Which application is best for geoprocessing?
Differences in the way that results are displayed in the
two applications may lead you to choose one over the other depending on the geoprocessing task. For example, if you are importing a shapefile to a geodatabase, you
may want to run the process in ArcCatalog so that you
can see the new feature class in the Catalog Tree. But if you are selecting
features, you may want to run the process in ArcMap
so that you can see the results in the map display.
In this
topic you'll get a chance to compare the different geoprocessing
methods. You'll also learn how to find tools, manage your toolboxes, and get
help when you need it.
Regardless
of what
There is
more than one approach you can take to determine which tool you need for a
certain job. As you saw in the previous topic, ArcGIS
geoprocessing tools are organized into logical groups
based on types of geoprocessing tasks. With that
knowledge, you can begin to narrow down your search. For example, suppose that
you need to join an attribute table to a feature class. The Data Management
Tools toolbox would be a good starting point. Once you think you've found the
right tool, you can read the tool's help to verify it works the way you think
it does.
You can also
use keywords to search all the tools in ArcToolbox to
find the tool you need. Alternatively, you can search ArcGIS
Desktop Help for information about tools, and then launch the tool directly
from there.
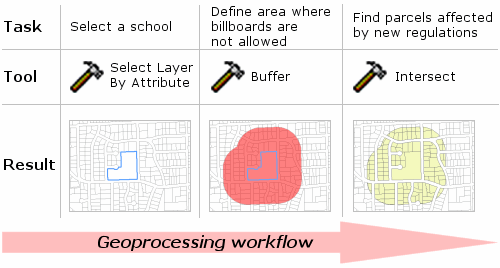
Although there are many geoprocessing tools to choose from, it's not difficult to
find the appropriate tools for your
![]() Complete tool reference
Complete tool reference
A complete list of all geoprocessing tools and a description of how each tool works can be found in ArcGIS Desktop Help under Geoprocessing > Geoprocessing tool reference. Here you will also find the ArcGIS Geoprocessing Commands Quick Reference Guide. The Reference Guide also tells you which tools are available with each type of ArcGIS license. This information can be particularly useful if you plan on sharing your work with others who may have a different license.