Relationship
classes
In a geodatabase, a relationship between two tables is stored in
a relationship class. Unlike ArcMap table joins and
relates, which are saved only in a map document, relationships stored in a
relationship class persist for the life of the relationship class.
Relationship
classes are created in ArcCatalog or using a geoprocessing tool. A relationship class can be created
inside a feature dataset or at the root level of the geodatabase;
the tables participating in the relationship class must be in the same geodatabase. If you delete a feature class or nonspatial table that participates in a relationship class,
then the relationship class is also deleted.
Once you
have created a relationship class, you cannot modify its properties (see next
point).
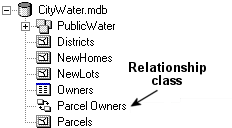
The ParcelOwners
relationship class was created at the root level of the CityWater
geodatabase and defines the relationship between the
Parcels feature class and the Owners table.
Only two
tables can be related in a single relationship class. To create a relationship
between more than two tables, you can set up a stacked relationship, where
table A is connected to table C through table B. To create a stacked
relationship, first create a relationship class relating table A with table B,
then create a second relationship class relating table B with table C.