Types
of attribute domains
There are
two types of attribute domains: range and coded value.
Range
domains
Range
domains can be created only for numeric fields—they specify acceptable minimum
and maximum values. For example, you could create a range domain for wells that
sets their valid depth values between 40 and 120 meters. Values can be either
integers or numbers with decimal places.
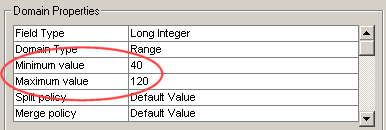
Range domains can be applied only
to numeric fields. When creating a range domain, you specify the minimum and
maximum values that will be allowed in the field.
When
editing in ArcMap, you can interactively validate
features that have a range domain by using the Validate Features command.
Validate Features checks the attributes of selected features and reports any
errors that are found. After running Validate Features, the features with
errors remain selected so their attribute values can be corrected.
Coded
value domains
Coded
value domains are explicit lists of acceptable values. They can be applied to
an attribute of any field type—for example, text, numeric, or date. Coded value
domains include both the code values and a more user-friendly description of
what the codes actually mean.
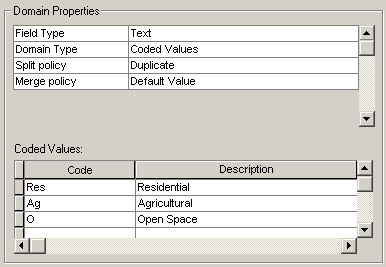
When creating a coded value domain,
you enter both the codes and a description for each.
In ArcMap, validation is automatic for coded value domains.
When you're editing an attribute that has a coded value domain, you cannot
manually enter an attribute value. Instead, you choose the desired value from a
dropdown list that contains the valid values.
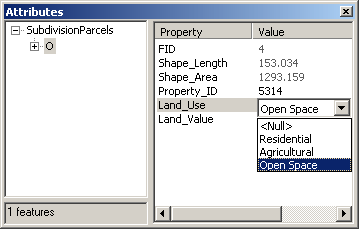
The codes are stored as values in
the database. The descriptions display in the ArcMap
Attributes dialog.