TIN to
features
TIN layers can be converted to two
different kinds of point layers and three different kinds of polygon layers.
Converting TIN data to features
allows you to use it in ArcMap for feature analysis
operations like buffer, intersect, clip, spatial join, and select by location.
Nodes to points (data nodes only)
Triangle nodes are converted to 3D point features. The point features
correspond to nodes within the TIN
zone of interpolation.
Nodes to points (all nodes)
Triangle nodes are converted to 3D point features. The point features
correspond to nodes inside and outside the TIN
zone of interpolation. (For instance, if you clip a TIN
and then convert all nodes to points, you will get points that were nodes in
the original unclipped TIN.)
Interpolation zone to polygon
The boundary of the TIN zone of
interpolation is converted to a single polygon feature.
Triangles classified by slope to
polygons
Triangles are converted to polygons with attributes that represent a slope
classification. By default, the TIN
slope renderer groups triangles into nine classes.
The conversion process creates a polygon layer with attributes ranging from 1
to 9.
Changing the classification
scheme of the TIN slope renderer before conversion will change the number of
polygons and their attributes in the output file.
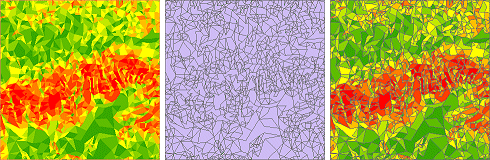
Left: A TIN
symbolized in ArcMap with the slope renderer. Middle: The TIN
converted to polygons classified by slope. Right: The polygon layer symbolized
with the slope color ramp.
Triangles
classified by aspect to polygons
Triangles are converted to polygons with attributes that represent an aspect classification.
By default, the TIN aspect renderer groups triangles into ten classes (N, NE, E, SE,
S, SW, W, NW, and N again, plus a class for flat slopes). The conversion
process creates a polygon layer with attributes ranging from 1 to 9 for the
directions, plus –1 (flat).
As with slope, changing the
classification scheme of the TIN aspect renderer
before conversion will change the number of polygons and their attributes in
the output file.
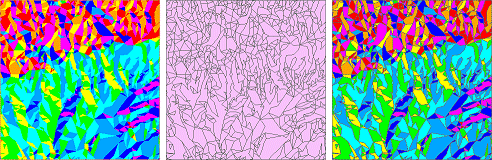
Left: A TIN
symbolized in ArcMap with the aspect renderer (hillshade illumination
is turned off). Middle: The TIN
converted to polygons classified by aspect. Right: The polygon layer symbolized
with the aspect color ramp.

