3D features
To display discrete geographic
features (like buildings, rivers, and wells) found on or beneath surfaces, 3D
Analyst makes use of a special kind of feature: the 3D feature. 3D features can
be stored in shapefiles or geodatabase
feature classes.
|
|
|
Buildings are a common type of 3D feature modeled with 3D
Analyst. |
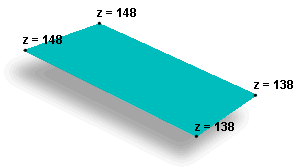
A 3D feature is a point, line, or
polygon that, in addition to its x,y
coordinates, stores a z-value as part of its geometry. A point has one z-value;
lines and polygons have a single z-value for each vertex in the shape.
|
|
|
Both 3D polygon and 3D line features store z-values in the
vertices. 3D points, of course, only have one z-value. |
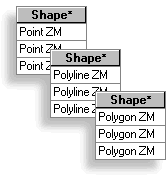
You can identify shapefiles
and geodatabase feature classes that store 3D
features by looking at the Shape field in their attribute tables. Those that
have z-values will end with ZM. For example, the attribute values found in the
Shape field for 3D point features will appear as “PointZM”.
|
|
|
3D feature classes can be identified by the ZM values in the
Shape field of their attribute tables. |
In ArcScene,
you can also render 2D features in 3D by manipulating their layer properties.