Defining
z and m domains
If you
want to store z or m values with a feature class, when you create the feature
class, you must specify that it will contain z or m values. You can also set
spatial domains for these values. As with x,y domains, the geodatabase
stores z and m values as integers between 0 and 2.14 billion.
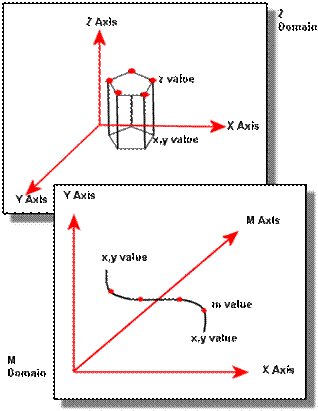
Geodatabases can store z and m values in
addition to x,y coordinate
values.
If you are
importing a coverage with m values (a route feature
class) or a shapefile with z coordinates (a 3D shapefile), then the minimum and maximum m or z values
default to the values in the source data. If you need to, you can change both
the value range and the precision value.
If you do
not import z or m domains, ArcCatalog will provide
placeholder values which you will probably want to modify. For example, the
placeholder minimum z and m domain values will not be a negative number. If you
were creating a z domain that needed to include negatives, such as elevations
below sea level, you would have to modify the z domain values.
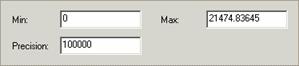
The same placeholder values are
provided for both z and m domains.
To modify
the z or m domain, enter the lowest value you will need for your data and a
precision value to support its accuracy.
While
feature classes within a feature dataset must share the same x, y, and z
domains, they can have different m domains.