Changing
the precision
If you
decide to modify the default values for the spatial domain when creating a
feature class or feature dataset, you will find that changes to the precision
value result in changes to the spatial extent values. Increasing the precision
value decreases the spatial extent, while decreasing the precision value
increases the spatial extent.
When you
change the precision value, the Max X and Max Y values automatically update to
reflect the change.
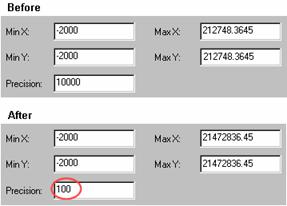
When you change
the precision, the spatial extent changes as well. In this example, when the
precision is decreased, the Max X and Max Y values update to increase the
allowed spatial extent.
You should
choose a precision value that will support the accuracy of your data. If you're
setting the precision for a feature dataset that will contain feature classes
of varying accuracy, you should use a precision value that will support the
highest level of accuracy.
![]() Precision considerations
Precision considerations
When choosing a precision value for storing your data,
consider the following general guidelines:
· Choose the smallest precision that
allows for updates to your data and anticipates future growth, and that
supports the highest level of accuracy required for the data.
· If you choose a precision that is
too small, the resolution of your data will be decreased and the shape of
features may become distorted. If you choose too large a precision, however,
your data may imply a higher level of accuracy than it possesses.
· The higher the precision value, the
larger the storage requirements for your data will be. High precision values
may also result in slower processing speed. This should only be a consideration
if you are working with very large datasets.
· An inappropriate precision can
affect the cluster tolerance for a topology. As the precision increases, the
possible maximum cluster tolerance decreases. Using a precision value that is
too high for your data may make the maximum cluster tolerance so small that it
becomes difficult to fix topology errors using the ArcMap
edit tools. You'll learn about topology and cluster tolerance in the next lab.
You can
calculate the precision value you need using the formula below:
![]()
For
example, if you want to store data at 10-centimeter resolution (in other words,
1 geodatabase storage unit = 10 cm) and your map
units are meters (convert meters to centimeters: 1 meter = 100 cm), your
formula will use the following values:
![]()