Precision
In a geodatabase, precision describes how your data will be
stored on your system. The geodatabase stores
coordinates as integers. ArcGIS uses the precision
value to convert the numbers with decimals to integers—the precision value
determines how many decimal places will be preserved when a coordinate is
converted to an integer. Up to nine decimal places can be preserved.
When
you're working with your data in ArcMap or viewing it
in ArcCatalog, precision is used to convert the
coordinates back to real numbers (numbers with decimals).
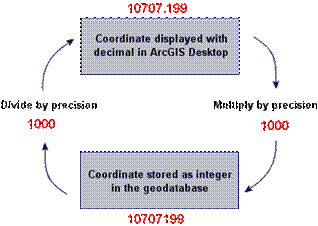
The precision value is used to
convert back and forth between the numbers with decimals displayed in ArcMap and ArcCatalog and the
integers stored in the geodatabase.
Together
with the coordinate values, the precision value defines the spatial domain of
your data. Increasing the precision value decreases the spatial extent and,
conversely, decreasing the precision value increases it. As the precision value
increases, so too does the data resolution that can be stored in the geodatabase.
For
example, a precision of 1,000 will store data at a higher resolution than a
precision of 100. If your data is stored in meters, a precision of 1,000 will
support data stored at millimeter accuracy. A precision of 100 will support
data stored at centimeter accuracy.
![]() Does higher precision equal higher accuracy?
Does higher precision equal higher accuracy?
It is important to understand that the precision value is
not a measure of the accuracy of your data. Accuracy is the measure of how
closely your data matches the true values in the real world. Using a higher
precision value will not increase the accuracy of your data. For example, if
your data has 1-meter accuracy, assigning a precision value of 1,000 will not
give your data millimeter-level accuracy.
When you
create a standalone feature class or feature dataset, ArcCatalog
will provide either a placeholder value or a default value for precision. In
both cases, the provided precision value will probably be higher than you need
for your data. You can accept the precision value or you can modify it if you
need to fine-tune your database.
After a
feature class or feature dataset has been created, you cannot change its
precision.