Understanding
spatial reference
When you
create a new feature class or feature dataset, you need to set the spatial
reference for the data it will contain. The spatial reference consists of the
coordinate system, spatial extent, and precision of the data.
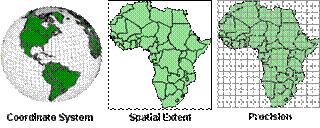
The spatial reference for a
standalone feature class or feature dataset is composed of a coordinate system,
the spatial extent, and a precision value.
You can
create a new spatial reference or import one from another spatial dataset. When
you import a spatial reference, you are provided with default values which will
often meet the needs of your data. If they don't, you can modify the default
values.
As you saw
in a previous concept, you can also create a new geodatabase
feature class by importing data stored in another spatial format. The spatial
reference associated with the data you're importing also imports with default
values that you can accept or modify.