Defining
the database structure
The basic
structure of a geodatabase consists of the feature
datasets, feature classes, and nonspatial tables into
which you organize your data, along with the attribute fields in feature class
tables and nonspatial tables.
There are
three ways to define the structure of a geodatabase.
You may use one or all of the methods when building a single geodatabase.
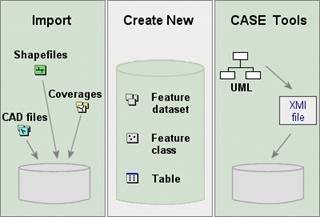
The three methods for defining the
structure of a geodatabases.
· Import existing data
ArcCatalog provides tools to help you import
existing data into a geodatabase. The data can be in
one of the supported data formats or in another geodatabase.
The import process creates new feature classes and tables. During import, you
can rename attributes or exclude them.
· Create the structure manually
You can use the wizards and tools provided in ArcCatalog to create new, empty feature datasets, feature
classes, and tables and define the attribute fields. You can combine this
method with the import method by manually creating a feature class and
importing just the structure from existing data.
· Use CASE tools
If you have an ArcEditor or ArcInfo license, you can use CASE tools to design and
create a geodatabase. CASE tools are most useful for
designing large, complex databases.
![]() Working with CASE tools
Working with CASE tools
CASE tools allow you to diagram the structure of the geodatabase using Unified Modeling Language (UML). UML is a
notation system that has become an industry standard for diagramming object models.
The steps for generating a geodatabase
schema are:
1.
Create
your geodatabase design using UML in Microsoft Visio
or Rational Rose.
2.
Export
the UML diagram to an XML Metadata Interchange (XMI) file or to a Microsoft
Repository, which stores the definition of all the UML elements.
3.
Add
the CASE Tools Schema Wizard to the ArcCatalog
interface, then use the Schema Wizard to generate the
feature datasets, feature classes, and tables from your UML diagram.
Many ArcGIS data models are
available as UML models in Visio format and can be downloaded from the ESRI
website and modified to suit your needs.
For detailed information about creating geodatabase schema with UML and CASE tools, see the ArcGIS Desktop Help (Contents tab -> Building a geodatabase -> Building geodatabases
with CASE tools).