Geometric
networks
In the
real world, examples of networks abound: streams joining together to form
larger streams, pipes carrying water to homes and businesses throughout a city,
and power lines carrying electricity.
In a geodatabase, you can model each of these real-world
networks with a geometric network. Created from point and line feature classes
grouped together in a feature dataset, geometric networks enable you to define
and analyze the flow of resources to answer questions such as:
· Which streams will be affected by a
proposed dam?
· Which areas will be affected by a
water main repair?
· What is the quickest route between
two points in the network?
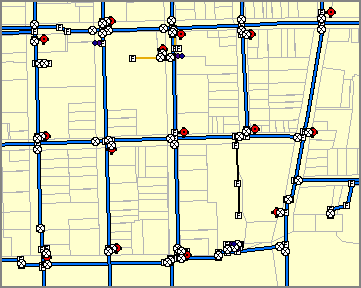
A water transmission network is
modeled in the geodatabase using a geometric network.
To create
and edit a geometric network, you need an ArcEditor
or ArcInfo license.
![]() Want
to learn more about geometric networks?
Want
to learn more about geometric networks?
In this course, you will not be working with geometric
networks. If you would like to learn more about geometric networks, you can
consult the ArcGIS Desktop Help (Contents tab -> Building a geodatabase -> Geometric networks).