What exactly is a geodatabase?
A geodatabase is a relational database that stores geographic
data.
At its
most basic level, the geodatabase is a container for
storing spatial and attribute data and the relationships that exist among them.
In a geodatabase, which is a vector data format,
features and their associated attributes can be structured to work together as
an integrated system using rules, relationships, and topological associations.
In other words, the geodatabase allows you to model
the real world as simply or complexly as your needs dictate.
Geodatabases are created, edited, and managed using the standard menus and tools in ArcCatalog™ and ArcMap™.
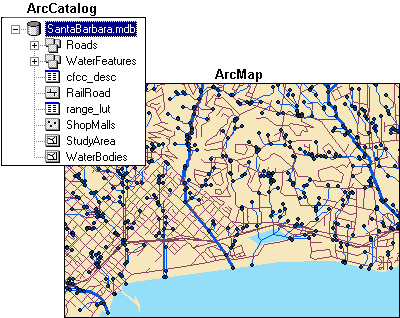
The data contained in the SantaBarbara geodatabase (SantaBarbara.mdb) is listed in the ArcCatalog Catalog tree and displayed in ArcMap.
Types of geodatabases
There are
two types of geodatabases: personal and enterprise
(enterprise geodatabases are sometimes called ArcSDE® geodatabases).
A personal geodatabase has the .mdb file extension (a format used by Microsoft Access) and can be read by multiple people at the same time, but edited by only one person at a time. A personal geodatabase has a maximum size of 2 gigabytes (GB). Vector data is stored in the database, while raster data is referenced.
Personal geodatabases are appropriate for smaller workgroups and for managing small to moderately sized datasets.
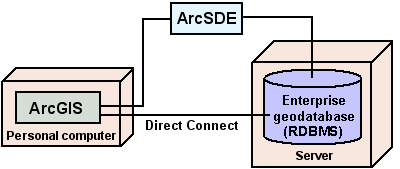
An enterprise geodatabase stores large spatial datasets using ArcSDE and a commercial database management system. Some database software allows for a direct connection between the ArcGIS application and the database.
If a project becomes too large for a personal geodatabase, you can easily move the data stored in a personal geodatabase to an enterprise geodatabase using ArcCatalog.
|
Table 1. Comparison of enterprise
and personal geodatabases |
|||||||
|
|
DBMS |
Client / Server |
Long Transactions* |
Disconnected Editing |
Editors |
Raster Data |
Size |
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
1 or
more at the same time |
Stored |
Unlimited |
|
Personal |
Microsoft
Access |
No |
No |
No |
1 at a
time |
Referenced |
Up to 2
GB |
*Database transactions spanning multiple edit sessions