Maintaining
spatial relationships
The edits
you make to the shape of one feature may affect the shape of another feature.
For example, if two features are adjacent, connected, or coincident with each
other, editing the shape of one will result in a change to the other's shape as
well. When you edit a feature's shape, it's important to make sure its spatial
relationships with other features do not become lost or distorted. If they do,
your database no longer reflects reality, and you will not be able to perform
accurate analyses.
Suppose
you move the boundary between two adjacent land parcels. During the move, you
leave a gap between the two features in the database that doesn't exist in the
real world. You have introduced inaccuracy into your database.
Or,
suppose you are editing a road feature that coincides with a bus route feature.
What would happen if, after editing the roads, the bus route went through a
building instead of following the road? Do you think the driver would mind?
Streams
are connected in the real world. What if you edited one and somehow
disconnected it from the others? An orphan stream is a lonely water body, and
soon dries up.
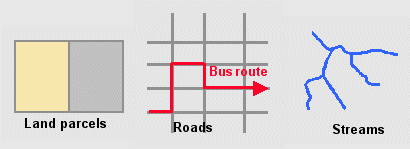
Spatial relationships between
features, such as those that exist between adjacent land parcels, coinciding
roads and bus routes, and connected stream features, need to be maintained
during editing.
ArcGIS
provides a way to prevent these problems. It is called topology. Topology
defines the spatial relationships among features and maintains them during
editing.
A simple
kind of topology is map topology. A map topology identifies and maintains
spatial relationships among features during an edit session. Map topology
allows you to simultaneously edit features that are spatially related—with map
topology, if you reshape a road feature, the coinciding bus route will be
reshaped as well.
Map
topology is available only during an edit session. To permanently maintain the
spatial relationships among features stored in a geodatabase,
you can use a geodatabase topology. A geodatabase topology is a set of rules and properties that
defines the spatial relationships you want to model and preserve in your data.
A geodatabase topology is a very useful tool for
maintaining the integrity of your database.
A geodatabase topology can only be created with an ArcEditor™ or ArcInfo® license. A
map topology can be created with ArcView®, ArcEditor, or ArcInfo.