Shapefiles
Shapefiles
are a file-based data format native to ArcView® 3.x software. Conceptually, a
shapefile is a feature class—it stores a collection of features that have the
same geometry type (point, line, or polygon), the same attributes, and a common
spatial extent.
Despite
what its name implies, a single shapefile is actually composed of at least
three files, and as many as eight. Each file has the shapefile name and an
extension. The three main files associated with a shapefile have the .shp,
.shx, and .dbf extensions. The information stored in these files allows the
features and the attribute table to be displayed.
![]() More about shapefile files
More about shapefile files
Every shapefile has the following three files:
· ShapefileName.dbf — dBASE-format
table that stores feature attributes
· ShapefileName.shp — stores feature
geometry
· ShapefileName.shx — stores the
index of the feature geometry
Files with the following extensions may also be included
with a shapefile:
· ShapefileName.aih — attribute index
file
· ShapefileName.ain — attribute index
file
· ShapefileName.prj — coordinate
system file
· ShapefileName.sbn — spatial index
file
· ShapefileName.sbx — spatial index
file
In
ArcCatalog you will see only the file with the .shp extension, but you can view
all the files associated with a shapefile in your operating system's file
manager (e.g., Windows Explorer). As with coverages, though, you should always
use ArcCatalog to manage shapefiles. ArcCatalog accesses all the files
associated with a particular shapefile when you rename, move, copy, or delete
the shapefile.
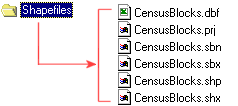
In Windows Explorer, the files
associated with a shapefile named CensusBlocks are visible.
Shapefiles
are a common data format and you will probably come across them on the Internet
or if you work with ArcPad® software or global positioning system (