Organizing
vector data
The basic
unit of the vector data model is the feature. Because it would be impractical
to digitally store every feature by itself, the vector data model provides a
way to organize them.
The basic
storage unit for features is called a feature class. A feature class is a
collection of features that share the same geometry type and the same
attributes and that are located within a common geographic extent.
For
example, all customer locations for a group of business franchises can be
organized into a point feature class named "Customers." All the roads
in a city can be organized into a line feature class named "Roads."
Areas in a city can be organized into a polygon feature class called
"Zoning."
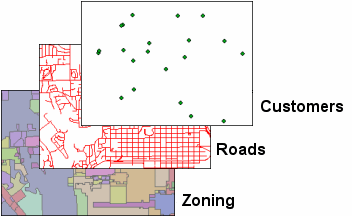
All features in a feature class
have the same geometry type, the same attributes, and are located within a
common geographic extent.
There are
three common vector data formats that use feature classes to store collections
of features: the geodatabase, coverage, and shapefile. You will learn about each of these data formats
next.