Polar (normal) aspect
Polar
aspect is the simplest form of planar map projections. The differences between
the three examples that follow are due solely to the position of the light
source. The center of the map projection can be either pole, and as a result of
this, parallels are represented as concentric circles and all meridians are
straight lines with true angles of orientation that converge at the poles.
Nearly all maps of
North polar aspect of a planar projection.
In the Gnomonic projection, parallels are unequally spaced. All great circles are shown as straight lines and therefore indicate the shortest path between two points, so it is commonly used for plotting flight paths. Distances measured from the center are true, but other measured distances are not. For example a straight line represents the shortest path, but measurements of the actual path are not true.
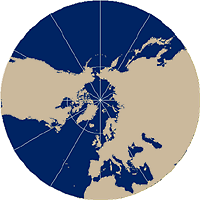
In polar Gnomonic map projections, all meridians are straight lines and parallels are circles.
In the
Stereographic and Orthographic projections, parallels are unequally-spaced
circles. The Stereographic projection is conformal and therefore commonly used
for mapping
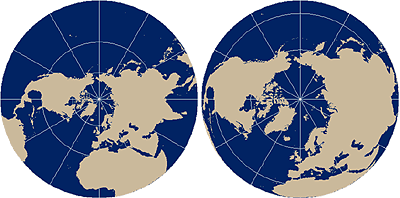
The polar Stereographic map projection (left) and the polar Orthographic map projection (right).