Equatorial aspect
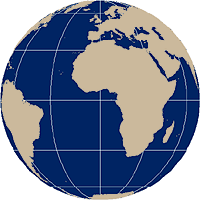
The planar equatorial aspect places the earth's equator in the center of the map projection. As with the polar aspect, the resulting differences between the three examples below are due solely to the position of the light source.
Equatorial aspect of a planar projection.
In the Gnomonic projection, all meridians are unequally-spaced straight lines, except for the meridians defining the circumference of the map projection. The equator is also a straight line perpendicular to the meridians, but all other parallels are hyperbolic arcs rather than circular arcs that become more concave as they approach the polar regions. Great circles are displayed as straight lines, as with the polar perspective, so navigation is still its primary application. But, as in the polar aspect, distance is distorted.
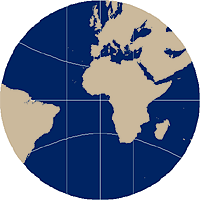
The equatorial gnomonic map projection maintains all meridians, except the meridian defining the circumference of the map projection, as straight lines.
In the Stereographic projection, only the central meridian of the map projection and the equator are straight lines and intersect at right angles. All other meridians are equally-spaced curved arcs converging as they approach the poles and all other parallels are unequally spaced with the geometric distance between them increasing as they approach the edge of the projection. Poles are represented as circular arcs rather than points. The equatorial aspect of the Stereographic projection is not frequently used today, but historically it has been used to represent either the western or eastern hemispheres.
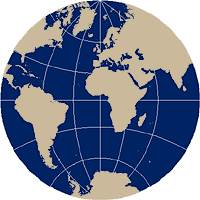
In the equatorial Stereographic map projection, only the central meridian and the equator are straight lines.
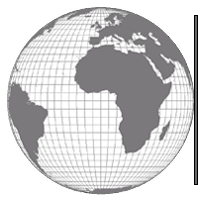
In the orthographic form, the central meridian for the map projection is a straight line intersecting the equator at a right angle while all other meridians are unequally-spaced elliptical arcs intersecting at the poles. All parallels are unequally-spaced parallel straight lines with the poles represented as points. Its main application is for displaying the earth as seen from space, but it's occasionally used as reference or location insets for maps.
In the equatorial Orthographic map projection all parallels are straight lines.