ArcMap
ArcMap is
the ArcGIS application you use to explore and edit geographic data, perform
analysis, and create professional-quality maps, graphs, and reports. When you
work in ArcMap, you work with a map document file, which has the .mxd file extension.
The ArcMap interface consists of the Table of Contents and the map display area, as well as a number of toolbars and menus for working with the map and its data. The order of layers within the Table of Contents is important; the layers at the top of the Table of Contents draw on top of the layers below them. Therefore, you should put the layers that form the background of your map, such as the ocean, at the bottom of the Table of Contents.
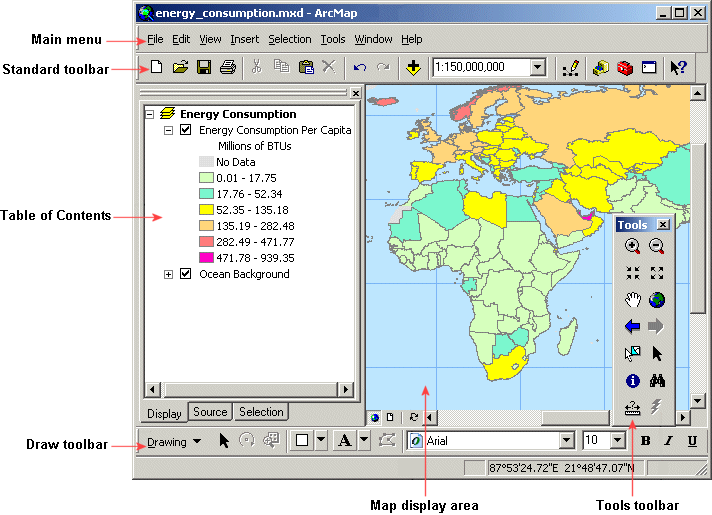
The ArcMap interface consists of the Table of Contents, the map display area, and easy-to-use menus and tools. The Table of Contents for this map includes two layers which are displayed on the right. The Tools toolbar is shown floating, while the Standard and Draw toolbars are docked to the ArcMap window. You can dock or float any of the toolbars.
In ArcMap, there are two views for working with data: data view and layout view. In data view, you explore, edit, query, analyze, and symbolize data. In layout view, you arrange data frames and add other map elements, such as scale bars, titles, and legends, to create a map layout that can be published in print or digital form. In data view, you can view only one data frame at a time. In layout view, you can view multiple data frames.
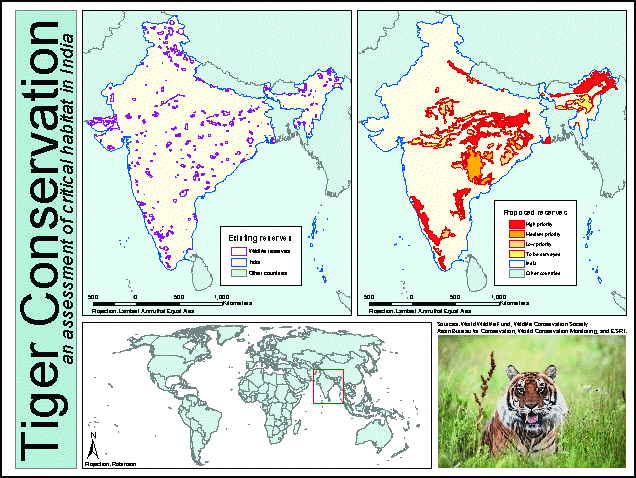
ArcMap provides tools for creating professional-looking
map layouts. This map layout includes three data frames, two legends, scale
bars, a title, and an image of a tiger.